The Impact of Complex Trauma on Brain Development and Recovery
FACT CHECKED ✅
This article explores how complex trauma affects brain development and functioning, drawing on recent research and insights. We delve into the brain’s remarkable ability to heal itself, identify the impacts of trauma on brain structure and function, and provide practical strategies for fostering brain health and recovery in individuals with Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (C-PTSD).
 |
| Complex trauma has a profound impact on brain structure and function (📷: Scientia) |
The human brain is an extraordinary organ, capable of adapting and healing even after significant trauma. C-PTSD often results from prolonged exposure to trauma, particularly during childhood. Today we examine the effects of complex trauma on brain development and functioning, highlighting the brain’s potential for recovery and offering practical strategies for fostering healing.
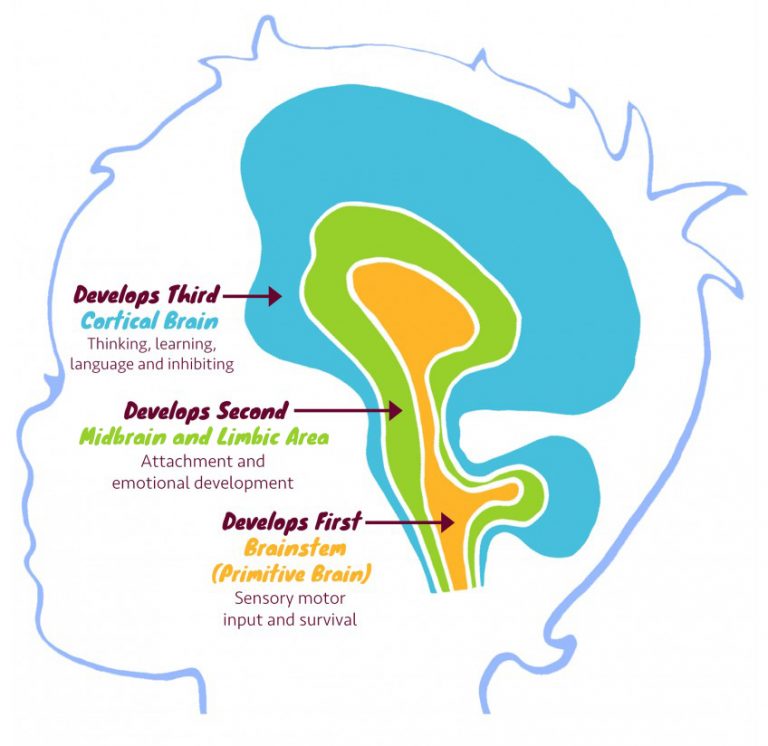 |
| Brain Development Stages (📷: nscc) |
Understanding Complex Trauma
Complex trauma differs from simple trauma in that it involves ongoing, repeated exposure to traumatic events. These experiences, which can range from physical/sexual abuse to emotional neglect, leave a profound impact on a child’s developing brain. Even in seemingly normal environments where basic needs are met, a lack of emotional safety and consistency can create a state of chronic insecurity, contributing to C-PTSD.
The Impact of Complex Trauma on Brain Development
Brain Size and Growth
Research has shown that children who experience neglect have smaller brains compared to those raised in nurturing environments. This difference is evident as early as three years old. The lack of stimulation and emotional connection in neglected children leads to stunted brain growth, affecting areas responsible for learning and emotional regulation.
 |
| Healthy vs Traumatised Child's Brain (📷: nypost) |
Developmental Stages and Trauma
The brain undergoes rapid growth from conception to age five, with significant development continuing until around age 25. Trauma during these formative years can disrupt the normal progression of brain development. The brain’s response to trauma includes heightened fear responses and an overdeveloped fight-or-flight mechanism, often at the expense of cognitive and emotional growth.
Brain Structure and Function
Complex trauma impacts the brain’s structure, particularly the right and left hemispheres. The right brain, responsible for emotional and implicit memories, tends to be overdeveloped, while the left brain, which handles logical thinking and explicit memories, may be underdeveloped. This imbalance can lead to difficulties in processing emotions and making rational decisions.
The Limbic System and Stress Response
The limbic system, which includes the amygdala, plays a crucial role in the brain’s stress response. In individuals with C-PTSD, the limbic system is often hyperactive, leading to heightened stress responses and difficulty regulating emotions. This hyperactivity is linked to the brain’s release of cortisol and adrenaline during stress, chemicals that prepare the body for immediate action but can be harmful when produced in excess over time.
Practical Strategies for Brain Healing
Self-Compassion and Mindfulness
Practicing self-compassion and mindfulness can help regulate the stress response and promote brain healing. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and grounding exercises can reduce cortisol levels and enhance emotional regulation.
Therapeutic Interventions
Therapies like Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT), and Attachment-Based Family Therapy (ABFT) have shown promise in addressing the impacts of complex trauma on the brain. Appropriate therapeutic interventions help individuals process traumatic memories and develop healthier attachment patterns.
Creating a Supportive Environment
A nurturing environment is crucial for brain healing. This includes establishing safe, supportive relationships, setting healthy boundaries, and engaging in regular self-care practices. Support from mental health professionals, family, and friends can provide the necessary emotional security for recovery.
 |
| A nurturing environment is crucial for trauma healing (📷: kerylegan) |
While the impacts of complex trauma on the brain are profound, the potential for healing is equally remarkable. Through understanding the effects of trauma and implementing strategies for brain health, individuals with C-PTSD can foster resilience and recovery. Embracing self-compassion, seeking therapeutic support, and creating a nurturing environment are key steps towards healing and a brighter future.
⭐⭐⭐


